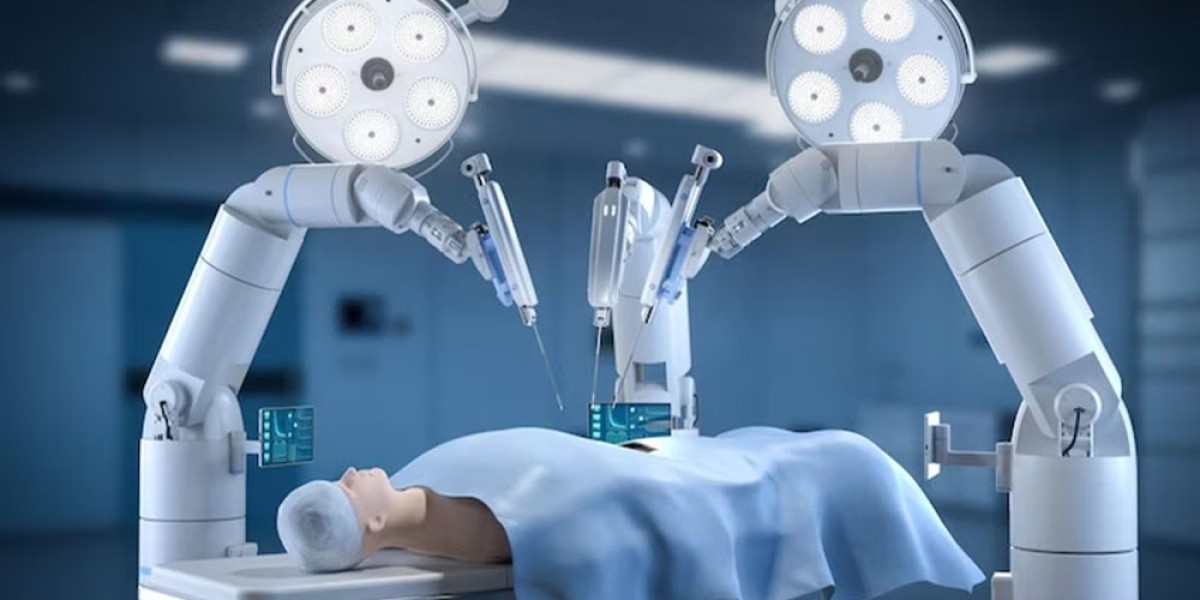
Enhancing Precision and Accuracy One of the most significant contributions of AI in robotic surgery is its ability to enhance precision and accuracy. AI-powered robotic surgical systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, use machine learning algorithms to improve instrument control, ensuring smoother and more precise movements. AI reduces hand tremors and refines delicate surgical maneuvers, allowing surgeons to perform intricate procedures with heightened accuracy.
AI-Assisted Decision-Making AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of medical data, including patient history, imaging scans, and real-time intraoperative data, to assist surgeons in decision-making. AI can predict potential complications, suggest optimal surgical approaches, and provide real-time guidance, thereby reducing human errors and improving patient outcomes.
Real-Time Image Processing and Augmented Reality AI enhances real-time imaging by processing and analyzing intraoperative images with superior clarity. AI-driven augmented reality (AR) overlays critical anatomical structures onto the surgeon's view, offering real-time guidance for precise navigation. This is particularly beneficial in procedures such as robotic-assisted neurosurgery and orthopedic surgery, where extreme precision is required.
Automation and Workflow Optimization AI enables partial automation of repetitive surgical tasks, such as suturing, tissue dissection, and instrument positioning. Robotic systems with AI assistance can perform these tasks consistently, reducing surgeon fatigue and allowing them to focus on complex decision-making. Furthermore, AI streamlines surgical workflows by predicting the next steps in a procedure, optimizing time efficiency in the operating room.
Predictive Analytics and Personalized Surgery AI-powered predictive analytics provide surgeons with insights into potential risks and complications based on patient-specific data. By analyzing historical surgical data and real-time inputs, AI can assist in developing personalized surgical plans, ensuring that procedures are tailored to individual patient needs. This approach minimizes surgical risks and improves overall patient outcomes.
Telesurgery and Remote Surgery Capabilities AI-driven robotic surgery has paved the way for telesurgery, allowing surgeons to perform operations remotely using robotic systems. Advanced AI integration ensures seamless communication between the surgeon and the robotic system, reducing latency and improving the precision of remote procedures. This technology expands access to expert surgical care, particularly in remote or underserved regions.
AI in Postoperative Monitoring and Recovery AI extends its impact beyond the operating room by assisting in postoperative monitoring and recovery. AI-powered systems analyze patient vitals, detect early signs of complications, and provide recommendations for post-surgical care. Wearable AI-integrated devices track recovery progress, enabling healthcare providers to intervene promptly when necessary.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations Despite its numerous advantages, AI in robotic surgery poses challenges, including data privacy concerns, cybersecurity risks, and regulatory hurdles. Ensuring the ethical use of AI in surgery requires strict adherence to guidelines, continuous validation of AI algorithms, and transparency in decision-making. Additionally, the cost of AI-driven robotic systems remains a barrier to widespread adoption, necessitating strategies for affordability and accessibility.
The Future of AI in Robotic Surgery The future of AI in robotic surgery is promising, with advancements in deep learning, robotic automation, and real-time data analytics. The development of autonomous surgical robots capable of performing complex procedures with minimal human intervention is on the horizon. AI-driven haptic feedback and smart robotic assistance will further refine surgical precision and patient safety.
Conclusion AI is redefining the landscape of robotic surgery, offering unparalleled precision, efficiency, and decision-making capabilities. By integrating AI-driven analytics, real-time imaging, automation, and telesurgery, robotic-assisted procedures continue to evolve, enhancing patient outcomes and surgical excellence. As technology advances, AI will play an increasingly critical role in shaping the future of robotic surgery, making minimally invasive procedures safer and more accessible worldwide.