Laparoscopic Myomectomy: A Minimally Invasive Approach for Uterine Fibroids
Introduction
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are non-cancerous growths in the uterus that affect millions of women worldwide. These fibroids can cause a variety of symptoms, including heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, frequent urination, and infertility. While several treatment options exist, laparoscopic myomectomy has emerged as a highly effective and minimally invasive surgical approach for removing fibroids while preserving the uterus.
What is Laparoscopic Myomectomy?
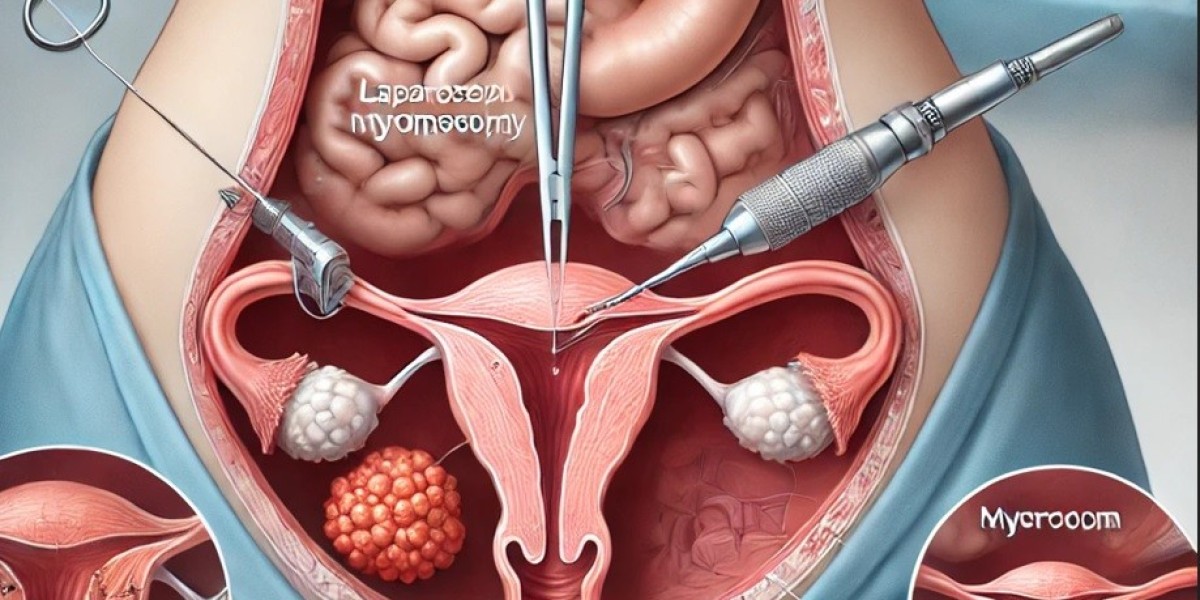
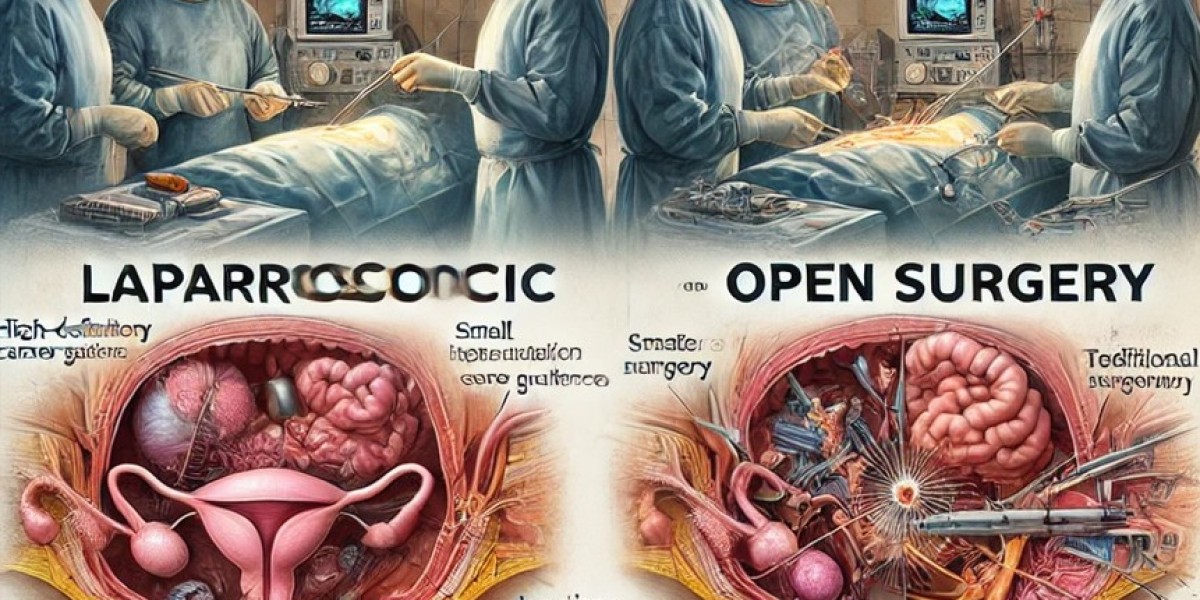
Laparoscopic myomectomy is a surgical procedure that removes uterine fibroids through small incisions in the abdomen. Unlike traditional open surgery, which requires a large abdominal incision, this technique utilizes a laparoscope—a thin, lighted tube equipped with a camera—to guide the surgeon in excising the fibroids with precision. Specialized instruments are inserted through additional small incisions to remove the fibroids while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Myomectomy
Minimally Invasive – Small incisions lead to reduced trauma to the body, minimizing blood loss and the risk of infection.
Faster Recovery – Patients typically experience a shorter hospital stay and a quicker return to daily activities compared to open surgery.
Less Postoperative Pain – Smaller incisions result in less pain and discomfort after surgery.
Uterine Preservation – Ideal for women who wish to maintain their fertility or avoid a hysterectomy.
Lower Risk of Adhesions – Compared to open surgery, laparoscopic procedures are associated with a reduced likelihood of scar tissue formation.
Who is a Candidate for Laparoscopic Myomectomy?
Laparoscopic myomectomy is suitable for women with fibroids that are not excessively large or deeply embedded in the uterine wall. The procedure is particularly beneficial for women who:
Experience moderate to severe symptoms due to fibroids
Wish to conceive in the future
Prefer a uterus-sparing procedure over a hysterectomy
Have fibroids that can be accessed and removed laparoscopically
The Procedure: Step-by-Step
Preoperative Preparation – Patients undergo imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI to assess the size, number, and location of fibroids.
Anesthesia – The procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
Incision and Access – Small incisions are made in the abdomen to introduce the laparoscope and surgical instruments.
Fibroid Removal – The fibroids are carefully excised and may be broken down into smaller pieces (morcellation) for easier removal.
Uterine Repair – The surgeon sutures the uterus to ensure proper healing and structural integrity.
Closure and Recovery – The incisions are closed with sutures or surgical glue, and the patient is monitored during recovery.
Postoperative Recovery
Recovery time varies among patients, but most can return to normal activities within two to four weeks. Postoperative care includes:
Managing pain with prescribed or over-the-counter medications
Avoiding heavy lifting and strenuous activities for a few weeks
Following up with the surgeon to monitor healing and discuss future reproductive plans
Potential Risks and Considerations
While laparoscopic myomectomy is generally safe, it carries some risks, including:
Bleeding and infection
Formation of adhesions
Possible recurrence of fibroids
Rare conversion to open surgery if complications arise
Conclusion
Laparoscopic myomectomy offers a highly effective, minimally invasive option for women suffering from symptomatic uterine fibroids. With advantages such as shorter recovery time, reduced pain, and uterus preservation, it has become a preferred choice for many patients seeking relief from fibroid-related symptoms. Women considering this procedure should consult with a gynecological surgeon to determine if it is the right option for them.