Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Benefits and Challenges Compared to Open Surgery
Introduction
Hysterectomy, the surgical removal of the uterus, is one of the most commonly performed gynecological procedures worldwide. Traditionally, this procedure was performed via open abdominal surgery, but advancements in minimally invasive techniques have made laparoscopic hysterectomy the preferred approach in many cases. Laparoscopic hysterectomy offers numerous advantages over open surgery, but it also presents unique challenges. This article explores the benefits, challenges, and comparative aspects of laparoscopic versus open hysterectomy.
Understanding Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Laparoscopic hysterectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which the uterus is removed using small incisions, a laparoscope (camera), and specialized surgical instruments. It can be performed as:
Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (TLH): The entire uterus, including the cervix, is removed laparoscopically.
Laparoscopic-Assisted Vaginal Hysterectomy (LAVH): The uterus is removed through the vagina with laparoscopic assistance.
Supracervical Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (SLH): The uterus is removed while preserving the cervix.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Hysterectomy Over Open Surgery
Compared to open (abdominal) hysterectomy, laparoscopic hysterectomy provides multiple benefits:
1. Minimally Invasive Approach
Uses small incisions rather than a large abdominal incision.
Results in less postoperative pain and quicker recovery.
2. Faster Recovery and Shorter Hospital Stay
Most patients go home within 24 hours, compared to a 3-5 day hospital stay for open surgery.
Faster return to daily activities within 2-3 weeks, compared to 6-8 weeks for open surgery.
3. Reduced Postoperative Pain and Blood Loss
Smaller incisions lead to less surgical trauma and reduced blood loss.
Lower risk of needing a blood transfusion.
4. Lower Risk of Infection and Adhesions
Laparoscopic surgery reduces exposure of internal organs, decreasing the risk of postoperative infections.
Less tissue handling leads to fewer adhesions and complications.
5. Improved Cosmetic Outcomes
Small, barely visible scars compared to a large abdominal incision.
Challenges and Limitations of Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Despite its advantages, laparoscopic hysterectomy presents certain challenges:
1. Longer Operating Time
Laparoscopic hysterectomy generally takes longer than open surgery due to the complexity of instrument manipulation and suturing.
2. Technical Complexity
Requires advanced surgical skills and experience.
Surgeons must be proficient in laparoscopic suturing, energy device usage, and visualization techniques.
3. Risk of Organ Injury
Possibility of bladder, bowel, or ureteral injury due to limited tactile feedback.
Requires careful intraoperative dissection and identification of anatomical structures.
4. Cost and Equipment Availability
Requires specialized instruments and laparoscopic equipment, which may not be available in all healthcare settings.
Higher initial costs, although it may reduce long-term hospitalization expenses.
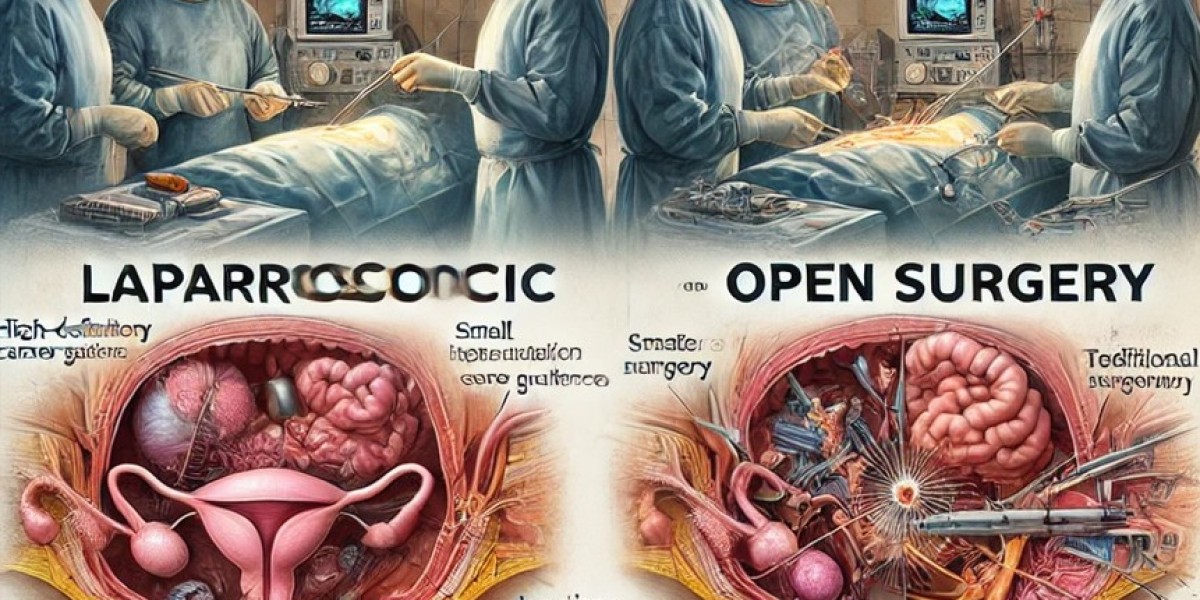
Comparison: Laparoscopic vs. Open Hysterectomy
| Feature | Laparoscopic Hysterectomy | Open (Abdominal) Hysterectomy |
|---|---|---|
| Incision Size | Small (5-10mm) | Large abdominal incision (10-15cm) |
| Hospital Stay | 24 hours | 3-5 days |
| Recovery Time | 2-3 weeks | 6-8 weeks |
| Postoperative Pain | Minimal | More significant |
| Blood Loss | Lower | Higher |
| Infection Risk | Lower | Higher |
| Adhesion Formation | Lower | Higher |
| Scarring | Minimal | Prominent |
| Surgical Expertise Required | High | Moderate |
Recent Advancements in Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (RALH): Enhances precision and control.
Fluorescence-Guided Surgery: Improves visualization of tissue perfusion.
AI-Assisted Navigation Systems: Enhances surgical decision-making.
Single-Incision Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (SILS): Further reduces scarring and recovery time.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic hysterectomy has revolutionized minimally invasive gynecological surgery, offering superior patient outcomes, faster recovery, and reduced complications compared to open surgery. However, it requires specialized training, advanced equipment, and careful surgical planning to minimize risks. With continued advancements in robotic technology and AI-assisted navigation, laparoscopic hysterectomy is expected to become even more efficient, accessible, and patient-friendly.
For the latest updates on minimally invasive gynecologic surgery, stay connected with the World Association of Laparoscopic Surgeons (WALS).