The Role of Laparoscopy in Trauma Surgery: Advancements and Limitations
Introduction
Laparoscopic surgery has significantly transformed the field of trauma surgery, offering minimally invasive alternatives to traditional open procedures. The ability to diagnose and manage abdominal trauma with smaller incisions, reduced morbidity, and faster recovery has made laparoscopy an essential tool in select trauma cases. However, its role in high-impact trauma and hemodynamically unstable patients remains limited. This article explores the advancements, benefits, and challenges of laparoscopy in trauma surgery.
Advancements in Laparoscopic Trauma Surgery
With continuous technological improvements, laparoscopy has expanded its applications in trauma surgery. Key advancements include:
1. Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities
Laparoscopy provides real-time intra-abdominal assessment, reducing the reliance on imaging alone.
It aids in the detection of occult injuries that may not be evident on CT scans.
2. Laparoscopic Hemostasis Techniques
Advanced energy devices (harmonic scalpel, Ligasure) enable precise bleeding control with minimal thermal spread.
Laparoscopic suturing and clip application allow for targeted hemostasis.
3. Minimally Invasive Organ Repair
Laparoscopic suturing for minor liver, spleen, and diaphragm injuries reduces the need for laparotomy.
Organ-preserving techniques minimize long-term complications and improve functional outcomes.
4. Laparoscopic Solid Organ Injury Management
Select cases of low-grade liver and splenic injuries can be managed laparoscopically, reducing splenectomy rates.
Hemostatic agents and topical hemostatic materials further improve outcomes.
5. Robotic-Assisted Trauma Surgery
Robotics enhances precision, control, and visualization, making laparoscopy more viable in trauma scenarios.
Allows for remote surgery applications in military and disaster settings.
Applications of Laparoscopy in Trauma Surgery
Laparoscopy is particularly useful in specific trauma scenarios, including:
Blunt Abdominal Trauma
Used for diagnosis and therapeutic intervention in stable patients.
Helps avoid unnecessary laparotomies when no significant injury is detected.
Penetrating Abdominal Trauma
Assists in determining peritoneal penetration and visceral injury.
Reduces non-therapeutic laparotomy rates, minimizing morbidity.
Diaphragmatic Injury Repair
Laparoscopy allows for direct visualization and repair of diaphragmatic tears, especially in left-sided trauma.
Prevents long-term complications such as diaphragmatic hernia.
Hollow Viscus Injury Assessment
Useful in detecting small bowel and colonic injuries, reducing missed injuries.
Facilitates primary repair in select cases without the need for conversion to open surgery.
Benefits of Laparoscopy in Trauma Surgery
Reduced postoperative pain and shorter hospital stay.
Lower infection rates compared to open surgery.
Minimized surgical trauma and improved cosmetic outcomes.
Faster return to normal function and activities.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite its benefits, laparoscopy has limitations in trauma surgery:
1. Hemodynamic Instability
Laparoscopy is contraindicated in unstable trauma patients due to the need for rapid intervention.
Pneumoperitoneum can worsen hypotension and compromise perfusion.
2. Limited Use in Severe Solid Organ Injuries
High-grade liver and splenic injuries often require open surgical intervention.
Laparoscopy is not suitable for massive hemorrhage control.
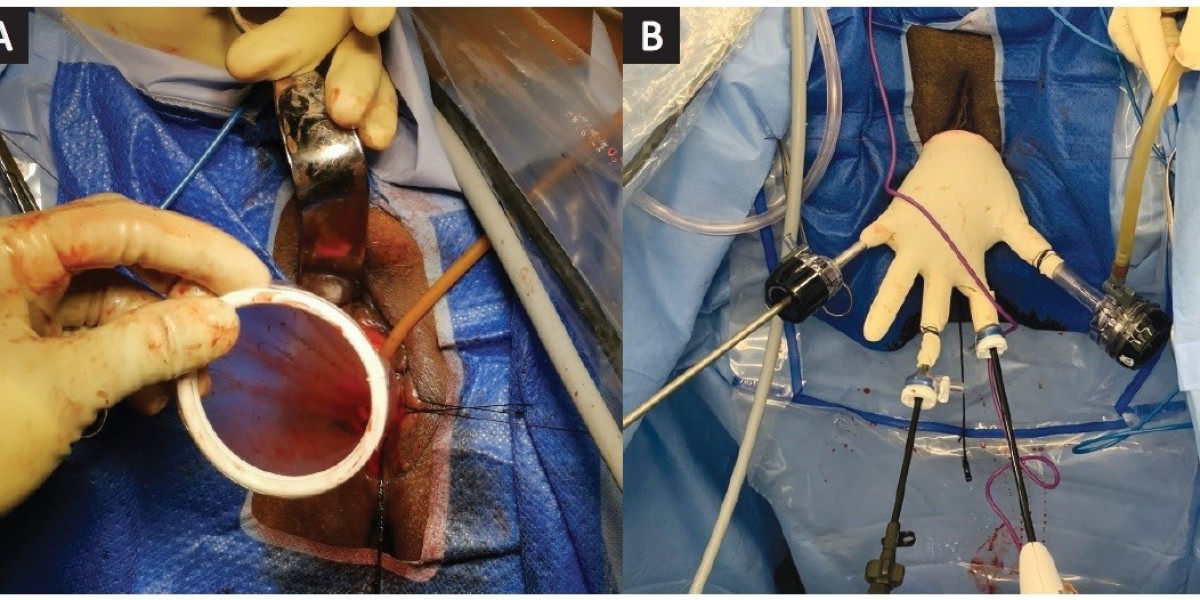
3. Technical Challenges
Requires advanced laparoscopic skills, particularly for bleeding control and suturing.
Limited working space in some trauma cases can restrict maneuverability.
4. Equipment and Resource Constraints
Not universally available in all trauma centers.
Requires specialized instruments and trained personnel.
Future Directions in Laparoscopic Trauma Surgery
The role of laparoscopy in trauma surgery is evolving with technological advancements. Future developments include:
AI-driven surgical navigation to improve real-time decision-making.
Improved hemostatic techniques, including bioactive dressings and laparoscopic vascular control.
Telesurgery applications for remote trauma care in battlefield and disaster zones.
Increased integration of robotic-assisted laparoscopic trauma surgery.
Conclusion
Laparoscopy has revolutionized trauma surgery by providing a minimally invasive approach for diagnosis and treatment in select cases. While it cannot replace open surgery for severe, hemodynamically unstable trauma, it offers significant advantages in stable patients with blunt and penetrating abdominal injuries. As technology and surgical expertise continue to advance, laparoscopy will play an increasingly important role in trauma care, improving patient outcomes while reducing surgical morbidity.
For further updates on laparoscopic advancements, training programs, and research in trauma surgery, stay connected with the World Association of Laparoscopic Surgeons (WALS).