Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: The Gold Standard for Gallbladder Removal
Introduction
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy has revolutionized the field of gallbladder surgery, emerging as the gold standard for gallbladder removal. This minimally invasive technique offers reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery, and minimal scarring compared to open cholecystectomy. It is now the preferred approach for treating symptomatic gallstones, chronic cholecystitis, and acute cholecystitis.
Indications for Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is recommended for patients with:
Symptomatic cholelithiasis (gallstones) causing biliary colic.
Acute cholecystitis, an inflamed gallbladder due to obstruction.
Chronic cholecystitis, leading to persistent gallbladder dysfunction.
Gallbladder polyps greater than 10mm, which have a potential risk of malignancy.
Biliary dyskinesia, a motility disorder causing biliary pain.
Gallstone pancreatitis, where gallstones block the pancreatic duct.
Surgical Technique
The laparoscopic cholecystectomy procedure is performed under general anesthesia and typically follows these key steps:
1. Patient Positioning and Trocar Placement
The patient is placed in a supine position with slight head-up tilt.
A pneumoperitoneum (CO₂ insufflation) is established to create working space.
Trocar placement includes one umbilical port (10mm) for the camera and three working ports (5mm each) for instrumentation.
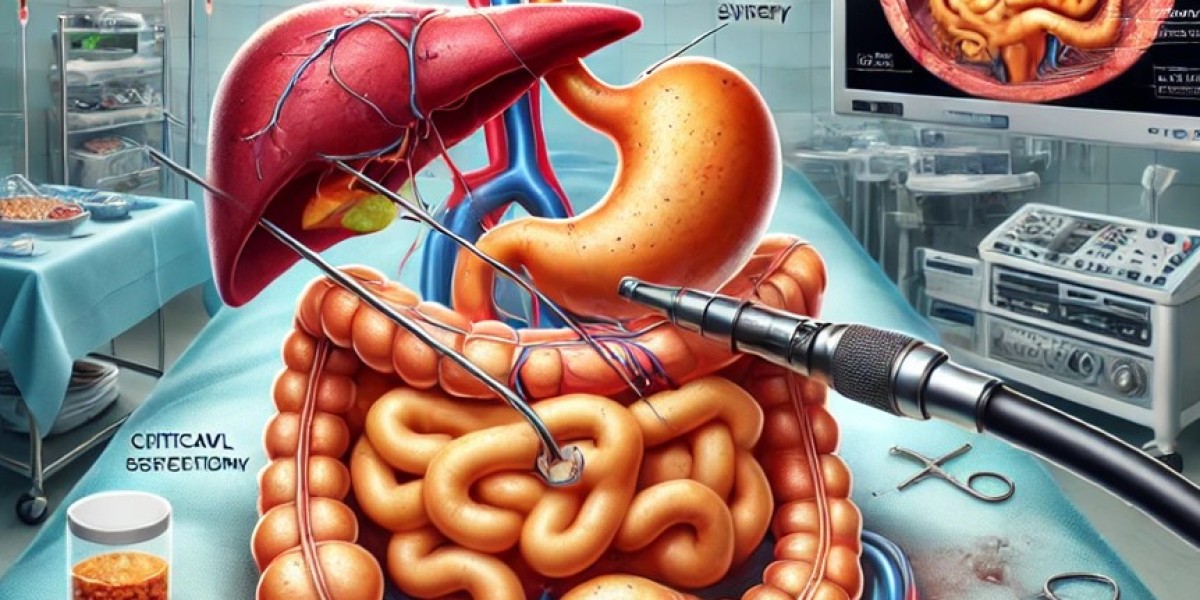
2. Identification and Dissection of the Calot's Triangle
The cystic duct and cystic artery are carefully dissected and isolated.
Critical View of Safety (CVS) is ensured to minimize the risk of bile duct injury.
3. Clipping and Division
The cystic duct and cystic artery are clipped and divided.
The gallbladder is then carefully dissected from the liver bed.
4. Gallbladder Extraction
The specimen is removed via the umbilical port.
The peritoneal cavity is irrigated, and hemostasis is ensured before closing the incisions.
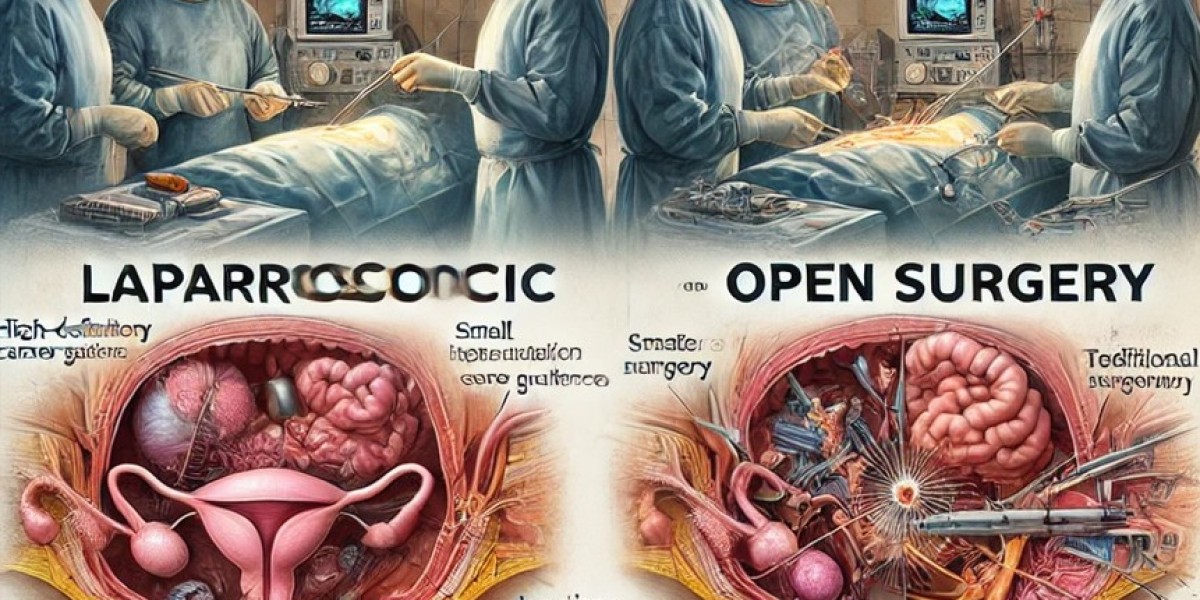
Advantages of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Compared to open cholecystectomy, laparoscopic cholecystectomy offers multiple benefits:
Minimally invasive with smaller incisions.
Reduced postoperative pain and discomfort.
Faster recovery, allowing patients to return to normal activities within a week.
Shorter hospital stay, often performed as a day-care procedure.
Lower risk of infections and postoperative complications.
Improved cosmetic outcomes with minimal scarring.
Potential Complications and Risk Factors
Although laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a safe procedure, complications may occur, including:
Bile duct injury (rare but serious, requiring surgical repair).
Bleeding and hematoma formation at trocar sites.
Gallbladder perforation, leading to bile spillage and peritonitis.
Conversion to open surgery in cases of excessive inflammation or anatomical difficulties.
Recent Advancements in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Single-Incision Laparoscopic Surgery (SILS): Uses a single umbilical port for improved cosmetic outcomes.
Robotic-Assisted Cholecystectomy: Provides enhanced dexterity and precision.
Fluorescence-Guided Imaging: Improves bile duct visualization, reducing the risk of injury.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
Patients are discharged within 24 hours post-surgery.
Early ambulation is encouraged to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Light diet is recommended initially, with a gradual return to a normal diet.
Full recovery is expected within 1-2 weeks.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy remains the gold standard for gallbladder removal due to its safety, efficiency, and patient-friendly approach. With continuous advancements, including robotic-assisted techniques and fluorescence-guided imaging, the procedure continues to evolve, offering improved outcomes and reducing surgical risks. For patients suffering from symptomatic gallstones or gallbladder diseases, laparoscopic cholecystectomy provides a minimally invasive, effective, and widely accepted solution.
For the latest updates in laparoscopic surgery and minimally invasive techniques, stay connected with the World Association of Laparoscopic Surgeons (WALS).